Verify and Test MapR Cluster
Intro
After installing a MapR Cluster, this post helps in :
- Verifying Cluster Status
- Run Post-Install Benchmark Tests
- Explore the Cluster Structure
Verify Cluster Status
The MapR Control System (MCS)
Connect
Open the MapR control system on https://<node ip address>:8443 on any of the control nodes.
Dashboard
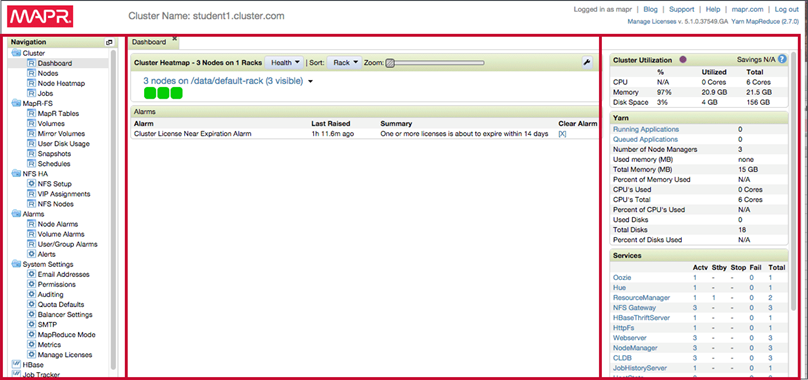
The dashboard view opens by default and there is a navigation pane on the left gives access to all MapR features. A Cluster Heatmap in centre gives colour coded overview of the health of each node
Heatmap
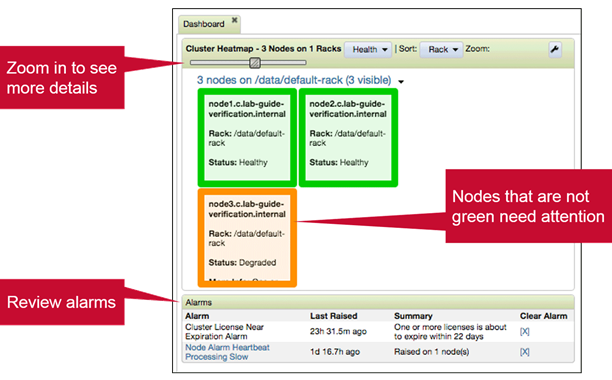
The Zoom Slider on the heatmap increases the size of icon for each node to see more details. Warnings will appear inside relevant node icon. Any alarms detected will be in the Alarms pane below the heatmap.
Services Pane
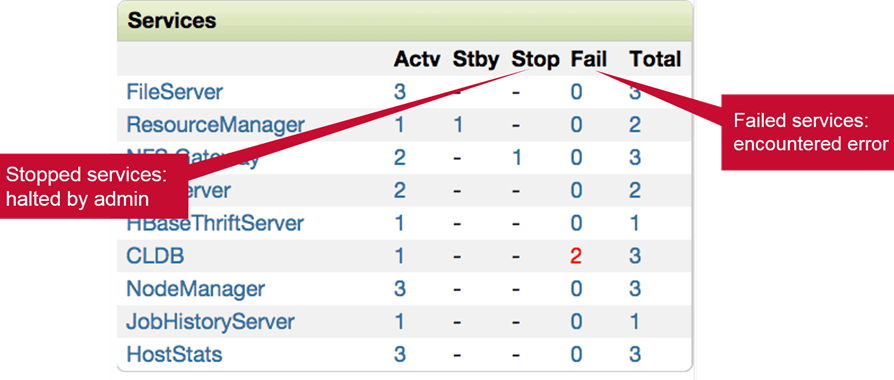
Services pane lists the services on the cluster. It will also display any failed or stopped services.
Using the Command-Line Interface (CLI)
When the cluster is up, hadoop commands can be run on the cluster. Alternatively we can also use maprcli to interact with the cluster.
- List Cluster Contents
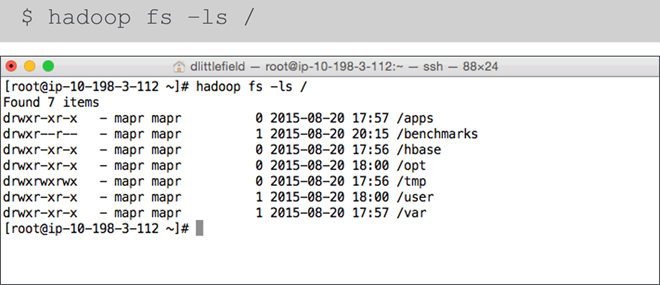
- List Nodes
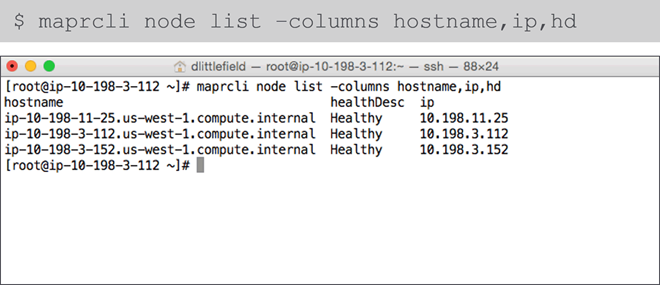
- List Services
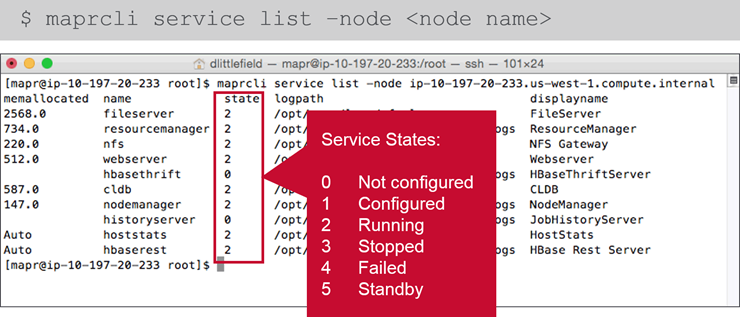
- Show Processes
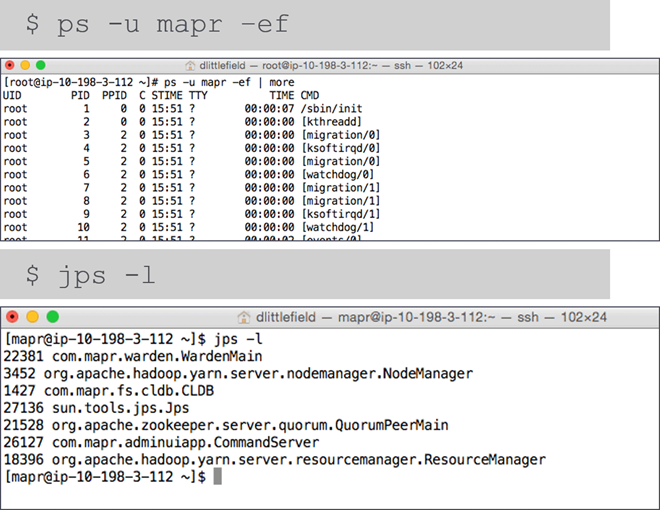
Visit MapR Documentation to see full list of maprcli commands.
Run Post-Install Benchmark Tests
Post-Installation Testing and Benchmarks
- Since its not feasible to test performance on each individual job; benchmarks are used as a proxy for workload.
- Use benchmarks to establish a baseline and test ongoing performance. The goal is to have performance in optimal range not stress to limits or underperform.
- Single benchmark tests won’t give whole picture; comparing different benchmarks will indicate expected performance.
Benchmark Types
There are two types of bench benchmarks.
- Synthetic Benchmarks
- Industry standard tests designed to see the max capabilities of a component.
- Exercise the system to see what it can do
- If you see a problem, you know it’s not the code but the hardware.
- Application Benchmarks
- Provide performance information on certain jobs to simulate the type of jobs you run on the system.
- Use the same data set each time
- Problems could be system components, or code
Verification Through the MCS
-
Cluster Utilization MCA can be used to monitor jobs and cluster performance. Monitor the heatmaps while the benchmarks are running to see how the cluster is performing like
Cluster UtilizationandYarnspecifications on the dashboard provides overall and realtime information on running Yarn jobs.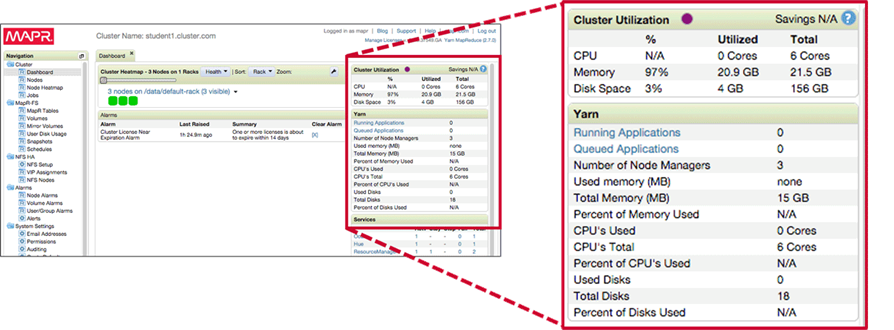
-
Node Performance Double click on a node to expand its properties and view its performance. Test and make changes iteratively to get best balance.
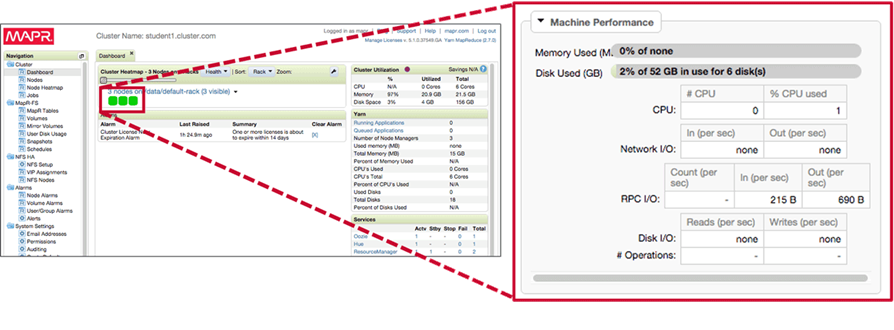
Synthetic Benchmark Tests
DFSIO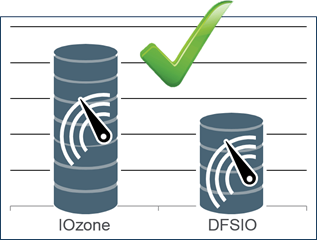
DFSIOcan be used to test reads and writes for the cluster- Runs a MapReduce job
- Provides an estimate of I/O performance
- Reasonable starting performance:
DFSIOresults at least 50% of maximum fromdisk-test.shrun as pre-installation checks. - IOZone is a destructive test and will ruin hadoop software if run post installation.
RWSpeedTest- Post-install test made available by MapR
- Provides aggregate read/write speeds for the node
- Unlike DFSIO, RWSpeedTest is not a MapReduce jobs
/root/post-install/runRWSpeedTest.sh
TeraGenandTeraSort- Comprehensive synthetic benchmark designed to measure upper limits of performance
- TeraGen generates data (run only once)
hadoop jar /opt/mapr/hadoop/hadoop-2.7.0/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.0-mapr-1506.jar teragen 5000000 /data/teragen-data - TeraSort sorts it ( run several times while tuning performance)
hadoop jar /opt/mapr/hadoop/hadoop-2.7.0/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.0-mapr-1506.jar terasort /data/teragen-data /data/teragen-output
Cascading and Remote Mirrors
Explore the Cluster Structure
-
Mounting the Cluster File System During installation, the cluster file system is automatically mounted to
/mapr/<cluster name>in localFS.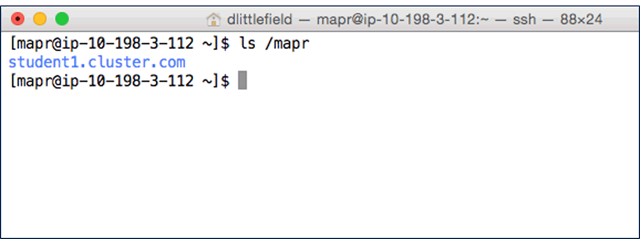
-
Cluster File System(Hadoop) Versus Local File System(Linux)
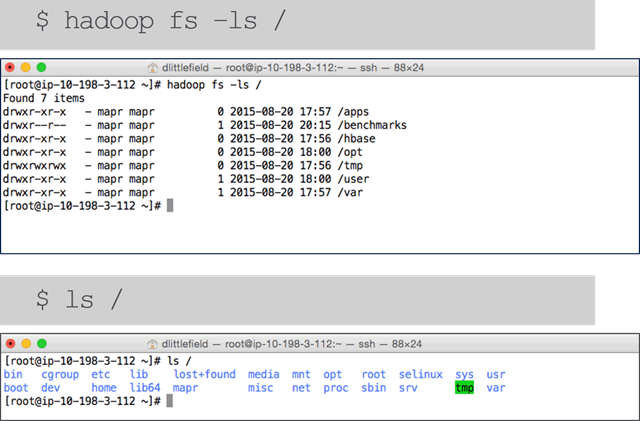
-
Since MapR mounts the HadoopFS to localFS it is possible to see the cluster filesystem with
lscommand.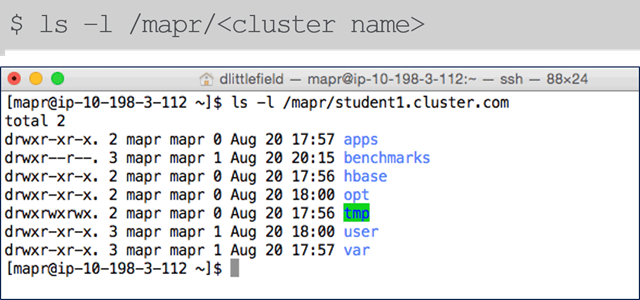
MapR System Volumes
Local Files and Directories
MapR also creates files and directories during installation. Some of them are listed here :


Leave a Comment